Repetitive Nerve Stimulation
What is Repetitive Nerve Stimulation?
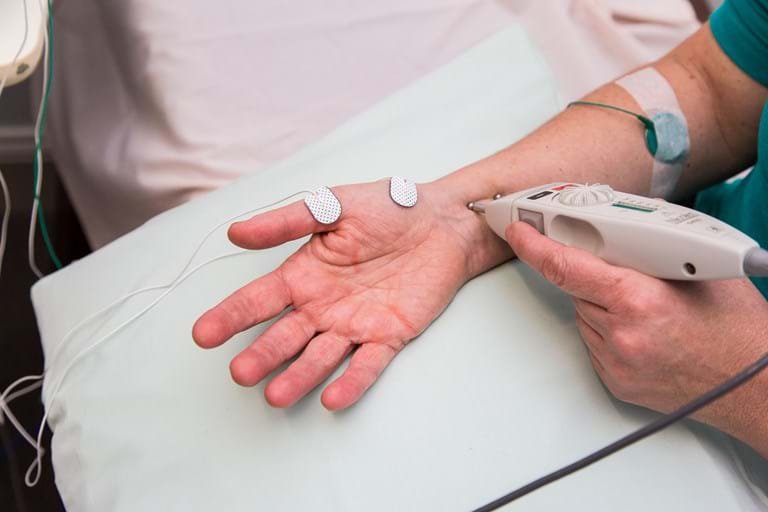
Repetitive Nerve Stimulation (RNS) is a specialized electrodiagnostic test designed to evaluate the function of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), where nerves communicate with muscles to facilitate movement. This test helps in identifying abnormalities in this critical connection, especially in conditions where the NMJ is compromised.
RNS is particularly valuable for diagnosing disorders that result in muscle weakness and fatigue, such as Myasthenia Gravis (MG), an autoimmune disease that disrupts communication between nerves and muscles, and Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome (LEMS), a rare condition often associated with cancer that impairs nerve signaling.
Why is RNS Important?
RNS is a critical diagnostic tool for detecting disorders affecting the neuromuscular junction. It allows physicians to identify conditions like MG and LEMS early, enabling timely treatment and improved management of symptoms. By assessing the communication between nerves and muscles under various conditions, RNS provides detailed insights that are essential for developing personalized treatment plans.
How to Prepare for the RNS Test?
The RNS test requires minimal preparation, but following these guidelines can help ensure accurate results and a smooth experience:
Clothing: Wear loose and comfortable clothing to allow easy access to your neck, shoulders, arms, or other areas being tested.
Skin Care: Avoid applying lotions, creams, or oils to the skin, as these can interfere with the placement and performance of electrodes.
Jewelry and Accessories: Refrain from wearing jewelry, such as rings, bracelets, necklaces, or watches, that might obstruct access to the testing areas.
Before the test begins, inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking, as certain drugs can influence NMJ function and test results.
Clothing: Wear loose and comfortable clothing to allow easy access to your neck, shoulders, arms, or other areas being tested.
Skin Care: Avoid applying lotions, creams, or oils to the skin, as these can interfere with the placement and performance of electrodes.
Jewelry and Accessories: Refrain from wearing jewelry, such as rings, bracelets, necklaces, or watches, that might obstruct access to the testing areas.
Before the test begins, inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking, as certain drugs can influence NMJ function and test results.
Are There Any Risks or Side Effects?
The RNS test is considered safe, with minimal risks or side effects. Most patients tolerate the procedure well. During the test, you may experience:
Mild Tingling: This sensation occurs as the electrical stimuli activate your nerves.
Muscle Twitching: The tested muscle may contract briefly, which is a normal response to the stimulation.
Slight Discomfort: Some individuals report a mild, temporary ache or fatigue in the tested muscle, but this subsides quickly after the test.
The RNS test is non-invasive, and no long-term side effects have been associated with the procedure. You can resume your normal activities immediately after completing the test.
Mild Tingling: This sensation occurs as the electrical stimuli activate your nerves.
Muscle Twitching: The tested muscle may contract briefly, which is a normal response to the stimulation.
Slight Discomfort: Some individuals report a mild, temporary ache or fatigue in the tested muscle, but this subsides quickly after the test.
The RNS test is non-invasive, and no long-term side effects have been associated with the procedure. You can resume your normal activities immediately after completing the test.

